 细胞培养进口血清进口胎牛血清进口新生牛血清进口猪血清马血清
细胞培养进口血清进口胎牛血清进口新生牛血清进口猪血清马血清 支原体检测盒及标准品常规PCR检测试剂盒荧光定量PCR检测(qPCR法)支原体DNA提取灵敏度标准品(方法验证用)特异性标准品(方法验证用)PCR定量标准品(可用于方法验证)
支原体检测盒及标准品常规PCR检测试剂盒荧光定量PCR检测(qPCR法)支原体DNA提取灵敏度标准品(方法验证用)特异性标准品(方法验证用)PCR定量标准品(可用于方法验证) 支原体祛除试剂细胞中支原体祛除环境支原体祛除水槽支原体祛除
支原体祛除试剂细胞中支原体祛除环境支原体祛除水槽支原体祛除 干细胞培养基
干细胞培养基 DNA/RNA污染祛除DNA/RNA污染祛除试剂DNA污染监测
DNA/RNA污染祛除DNA/RNA污染祛除试剂DNA污染监测 RNA病毒研究试剂RNA病毒检测试剂盒病毒RNA提取
RNA病毒研究试剂RNA病毒检测试剂盒病毒RNA提取 PCR仪器及配套产品DNA污染监测祛除PCR/qPCR仪性能检查PCR试剂PCR试剂盒PCR预混液(冻干粉)热启动聚合酶MB Taq DNA
PCR仪器及配套产品DNA污染监测祛除PCR/qPCR仪性能检查PCR试剂PCR试剂盒PCR预混液(冻干粉)热启动聚合酶MB Taq DNA 微生物PCR检测食品检测类产品食品微生物检测细菌PCR检测
微生物PCR检测食品检测类产品食品微生物检测细菌PCR检测
- 细胞培养进口血清进口胎牛血清进口新生牛血清进口猪血清马血清
- 支原体检测盒及标准品常规PCR检测试剂盒荧光定量PCR检测(qPCR法)支原体DNA提取灵敏度标准品(方法验证用)特异性标准品(方法验证用)PCR定量标准品(可用于方法验证)
- 支原体祛除试剂细胞中支原体祛除环境支原体祛除水槽支原体祛除
- 干细胞培养基
- DNA/RNA污染祛除DNA/RNA污染祛除试剂DNA污染监测
- RNA病毒研究试剂RNA病毒检测试剂盒病毒RNA提取
- PCR仪器及配套产品DNA污染监测祛除PCR/qPCR仪性能检查PCR试剂PCR试剂盒PCR预混液(冻干粉)热启动聚合酶MB Taq DNA
- 微生物PCR检测食品检测类产品食品微生物检测细菌PCR检测
|
|
预防和清除支原体污染的细胞培养方法2016-10-09 12:47
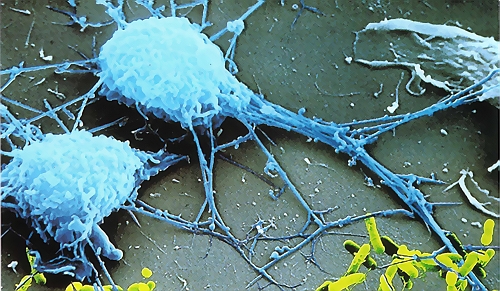 Since one of the main sources of mycoplasma is the cell cultures brought from outside, it is suggested to supply cells from reliable cell banks. In the case of the existence of mycoplasma contaminated cell culture in quarantine and the absence of separate incubators, only flasks in a plastic box with lid should be used. Never use plates and unsealed dishes in quarantine. In the case of suspected cultures, handling them at the end of the workday after all other cell culture work is completed, using separated media and reagents, and finally disinfecting the laminar flow hood after working is strongly suggested . Only use antibiotics responsibly Although ideally antibiotics used for cell culture should eradicate all contaminants, be nontoxic for the host cells and not interfere with experiments, none of the available antibiotics meet the mentioned criteria. Therefore, application of antibiotics in cell culture should be limited. Instead, a good aseptic practice plays an important role in prevention of contamination. Microbial contamination in cell culture which is antibiotic free is detectable by turbidity or color changes in cell culture medium. In the case of using antibiotics in a cell culture, there are four possibilities: 1. susceptibility to antibiotics, 2. resistance to antibiotics, 3. partial resistance to antibiotics, 4. resistance to antibiotics only by mycoplasma. The last one is the worst contamination since mycoplasmas can be spread by aerosols. In the case of antibiotic susceptibility, antibiotics prevent the cultivation of bacteria and fungi, but are incapable of precluding mycoplasma from the beginning. Therefore, continuous use of antibiotics for a long time in cell cultures not only is not helpful, but also can cause more problems. However, the use of antibiotics (Penicillin/ Streptomycin) for a short term (the first two weeks) in primary culture is vital. Since antibiotics are unstable in the medium, it is highly suggested to replace antibiotic containing medium with fresh medium every two or three days . Discard or treat mycoplasma contaminated cells In the case of mycoplasma contamination of cells which are really valuable and rare, it is suggested to treat them to eliminate mycoplasma infection. Otherwise, it is recommended to discard mycoplasma contaminated cells since they are considered as a source of contamination in the lab .
|
 细胞培养进口血清
细胞培养进口血清 支原体祛除试剂
支原体祛除试剂 干细胞培养基
干细胞培养基


